Maintaining Optimal CO2 Levels in an Aquarium
Introduction: The Importance of CO2 in Aquariums
When setting up a healthy aquarium, many factors come into play, but one element often overlooked is CO2 (carbon dioxide). CO2 plays a crucial role in supporting aquatic plants by aiding photosynthesis, which is essential for their growth. Plants in an aquarium not only enhance its aesthetic appeal but also contribute to oxygenation, helping maintain a balanced environment for fish and other aquatic life.
Maintaining the correct CO2 levels in your aquarium ensures that plants thrive, while fish and other organisms remain healthy. Without enough CO2, plants may not grow properly, leading to poor water quality and an unhealthy tank ecosystem.
Understanding CO2 Requirements for Your Aquarium
Every aquarium has different CO2 needs based on factors such as tank size, plant density, and the type of fish you keep. For instance, a densely planted freshwater aquarium will require more CO2 than a tank with minimal vegetation. The needs of saltwater tanks may vary, with different species of marine plants and animals requiring specialized CO2 management.
In general, a standard aquarium requires CO2 levels between 15-30 mg/L, but it’s important to tailor your CO2 dosage according to your tank's specific needs. A tank with heavy plant growth will benefit from higher CO2 levels, while a tank with minimal vegetation might require less. The type of fish you keep also impacts your CO2 needs, as some species are more sensitive to CO2 fluctuations.
How to Measure CO2 Levels in Your Tank
Monitoring CO2 levels in your aquarium is essential to ensure that plants are getting the right amount for healthy growth. There are several tools available to help you measure CO2 levels:
Drop Checker: A popular and easy-to-use tool that helps visually monitor CO2 levels by changing color according to the concentration of CO2 in the water.
CO2 Test Kits: These kits usually contain a solution that changes color when exposed to CO2, giving you a quantitative measurement of CO2 levels.
pH/CO2 Chart: By monitoring the pH of your aquarium water, you can estimate the CO2 concentration using a pH/CO2 chart.
Testing regularly is key to preventing imbalances in CO2 levels, which can be harmful to both plants and aquatic life.
Methods for Injecting CO2 into Your Aquarium
There are a few different ways to inject CO2 into your aquarium, each with its own set of benefits and considerations:
CO2 Cylinders: The most common method for aquariums with significant plant growth. CO2 cylinders provide a steady and controllable flow of CO2, but they require a regulator and regular refills.
CO2 Diffusers: These devices break the CO2 gas into tiny bubbles, allowing for better absorption into the water. They work well in both large and small tanks, providing consistent CO2 delivery.
Liquid CO2 Additives: Liquid CO2 products are easy to use and don’t require specialized equipment, making them a good choice for smaller or low-maintenance tanks. However, they tend to be less effective than CO2 cylinders for tanks with heavy plant growth.
Selecting the right CO2 injection method depends on your aquarium’s needs, tank size, and budget. Larger, heavily planted tanks will benefit more from CO2 cylinders, while smaller tanks or beginner setups may do well with liquid CO2.
How to Adjust CO2 Levels Effectively
Once you’ve set up your CO2 system, it’s important to monitor and adjust the levels as needed. There are a few signs that indicate whether CO2 levels are too high or too low:
Signs of Low CO2 Levels:
Yellowing leaves or slow plant growth.
Increased algae growth due to insufficient CO2 for plants.
Fish showing signs of stress, such as gasping for air at the water's surface.
Signs of High CO2 Levels:
Fish appearing lethargic or struggling to breathe.
Fish gathering near the surface of the water, trying to get more oxygen.
If you notice signs of imbalance, it’s important to take action promptly. You can adjust CO2 levels by tweaking your CO2 injection rate, increasing water movement to help distribute CO2 more evenly, or by using a CO2 controller to maintain a stable level.
Maintaining Stable CO2 Levels
Stability is key to maintaining a healthy aquarium. Fluctuating CO2 levels can harm both plants and fish, so it’s important to strive for consistency. Here are some tips for maintaining stable CO2 levels:
Use a CO2 Controller: These devices help regulate CO2 levels by turning the CO2 system on and off at set intervals.
Keep the Room Temperature Stable: Changes in temperature can affect CO2 solubility in water, causing fluctuations in CO2 levels. Keep the aquarium in a stable environment to reduce this issue.
Check Equipment Regularly: Ensure that all components of your CO2 system, such as the regulator, diffuser, and tubing, are working properly. Any malfunction can lead to CO2 imbalance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in CO2 Management
While managing CO2 in your aquarium, there are a few common mistakes you should avoid:
Over-injecting CO2: Too much CO2 can suffocate fish and cause them to exhibit signs of distress. Always monitor CO2 levels and avoid excessive injection.
Under-injecting CO2: If you don’t provide enough CO2, plants may suffer, leading to poor growth and unhealthy tank conditions.
Ignoring Plant and Fish Behavior: The health of your plants and fish provides valuable insight into your CO2 levels. If your plants are struggling, or your fish are stressed, take it as a sign to reevaluate your CO2 levels.
Conclusion: Achieving a Balanced CO2 Environment
Maintaining optimal CO2 levels is essential for a thriving aquarium. By understanding your aquarium's specific CO2 needs, measuring levels accurately, and using the right injection methods, you can create a healthy, stable environment for both plants and fish. Regular testing and adjustments will help ensure that your aquarium remains balanced and beautiful.
FAQ
Q1: What is the ideal CO2 level for my aquarium?
A: The ideal CO2 level typically falls between 15-30 mg/L for a balanced aquarium. However, this can vary based on plant density and fish species.
Q2: How often should I test CO2 levels?
A: It’s recommended to test CO2 levels at least once a week, especially when first setting up your aquarium or adjusting CO2 injection rates.
Q3: Can I use liquid CO2 instead of a CO2 cylinder?
A: Yes, liquid CO2 additives are a convenient option for smaller tanks or beginners, though they may not be as effective for heavily planted aquariums.
Q4: How can I fix high CO2 levels?
A: Reduce the CO2 injection rate, increase aeration in the tank, or use a CO2 controller to regulate the levels more consistently.
Q5: What happens if CO2 levels are too low?
A: Low CO2 levels lead to poor plant growth, increased algae, and stressed fish. Regularly monitoring and adjusting CO2 levels can prevent this.
 Innovative Features of Modern
Innovative Features of Modern
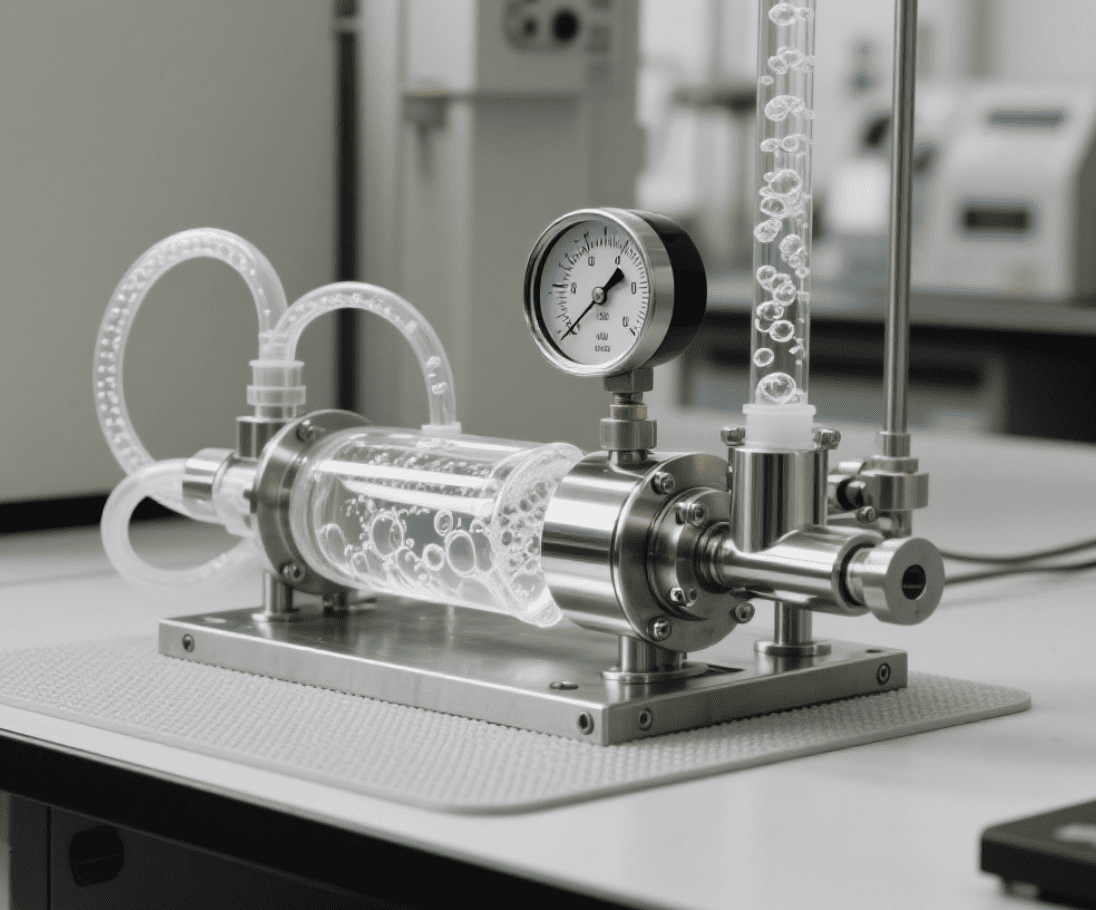 The Science Behind Carbonated
The Science Behind Carbonated
 How to Care for Carbonated Sod
How to Care for Carbonated Sod
 The Evolution of Carbonated So
The Evolution of Carbonated So